Blog Vertex AI: Serving architecture for real-time machine learning
By Insight Editor / 1 Dec 2022 / Topics: IT optimization , Automation , Cloud , IT modernization
Note: This post first appeared on November 30, 2022, on the Engineering Blog for SADA, An Insight Company on Medium.
Deploying machine learning algorithms for real-time inference is of utmost importance to power customer-facing web applications and other use cases. One of the prerequisites for a functional real-time ML serving architecture is to containerize the applications. Containerizing the runtimes provides a reproducible environment to train and deploy the ML models.
Deploying custom containers on Vertex AI in Google Cloud Platform (GCP) provides flexibility to add all the runtime-related dependencies. Some data science teams also tend to build and distribute ML models as Python packages. Due to the ubiquitous nature of Python as the chosen programming language for all data science applications, some teams find this level of abstraction adequate. However, containers provide the robustness and functionality to seamlessly expand the scope of ML models from training to production-ready.
In this article, we’ll look at some best practices and the process of deploying machine learning models using custom containers for real-time inference.
Serving framework and infrastructure
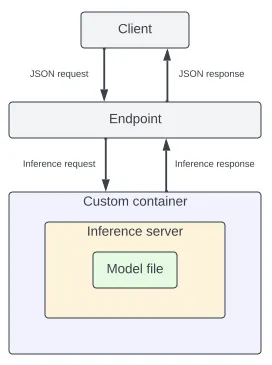
Converting a machine learning model to generate inferences in real-time in a production environment requires the following:
- Machine learning model (model file based on ML library)
- HTTP serving application
- Container with related dependencies with an appropriate entrypoint
There are several libraries available for developing a varied range of machine learning models, including Scikit-learn, Tensorflow, PyTorch and others. Google Cloud Vertex AI also provides standard runtimes based on the version of the underlying ML library.
There are several ways to wrap the ML model using a serving application. The compatibility matrix below lists various ways to do it:
Serving framework
ML library
| Serving framework | ML library |
|---|---|
| KServe | Scikit-learn, XGBoost, PyTorch |
| TFServe | Tensorflow |
| TorchServe | PyTorch |
If your runtimes can be sufficiently covered by using one of these libraries, it simplifies the process of containerizing the ML application. As mentioned earlier, building custom containers provides the ultimate flexibility to design the runtimes in any way we want.
Testing real-time ML models
Borrowing best practices from traditional web application development, the key to deploying real-time ML models is to set up a CI/CD process capable of releasing new features and products seamlessly. Creating an array of test suites is an integral part of setting up a CI/CD process. However, the testing requirements for ML models are quite different from traditional web apps. The array of test suites can be broken down into the following categories:
- Model functional testing: Covers pure Python unit tests. This tests the model output and processing logic embedded in the ML model. Pytest and unittest packages are popular choices.
- Model integrity testing: Generate predictions from your ML model based on a select, hand-crafted “golden dataset” that is representative of your feature space. This subset of data demarcates a baseline performance for the model. Subsequent versions of models trained and retrained from new data should perform at least as well as the baseline performance.
- Integration testing: Covers the integration between the machine learning model and any application consuming the real-time inferences. These smoke tests look for appropriate status codes and responses when calling HTTP endpoints.
- Model load testing: ML models can have high computational loads compared to regular web applications. It is important to load test the ML model framework to characterize the latencies, resource usage and autoscaling behavior. This characterization will determine the usability of an ML model for end customers.
Features for an MLOps serving framework
The Vertex AI offering from GCP includes functionality that is designed to help you start from scratch to train the models and deploy them for production readiness. In addition to deploying models for real-time inference, a few custom features and services are required to complement it:
- Intermediate “pass-through” application to proxy all calls to Vertex AI: Instead of exposing the Vertex AI endpoints directly to other applications, an intermediate application can serve as a single point of contact. This application can implement a central API contract for proxying all the calls to Vertex that can be uniformly distributed to several downstream applications, implement authentication and streamline new model deployment processes.
- Retraining models: As your ML model sees new data in production, it is important to retrain the model to correct for drift and bias. A full-fledged retraining framework is essential to automate the retraining process in order to curate and label new training data, tune hyperparameters, and validate the new model. Currently, there are a few approaches to retraining the ML model in production.
- A/B testing model versions: A/B testing of new model versions goes hand-in-hand with retraining models. Before routing all traffic to the new model version, a portion of the production traffic can be split and served to the new version. Performance of the old and new versions can be compared to finally promoting the new version. This feature is provided by Vertex AI out-of-the-box. A Vertex endpoint can proxy many models behind it.
Conclusion
Deploying machine learning algorithms to generate real-time inferences is a constantly evolving field. This particular task spans multidisciplinary efforts and coordination from data scientists to operations engineers and everyone in-between to pull it off. Vertex AI simplifies the operational overhead and deployment process in the data science stack. We have outlined some of the best practices we follow at Insight Engineering to build a robust and performant machine learning pipeline, and we hope these insights are useful for you on your own machine learning journey.
About Subash Padmanaban
Subash Padmanaban is a Senior Data Engineer at Insight. His background and experience is in building scalable data and machine learning pipelines.



